E-cigarettes have now officially been linked to worse case lung problems; the first case study on vaping has released alarming statistics over a three year period. But should it be compared to the destructive harm normal cigarette smoking produces to the human body?

In 1963, Hilbert A. Gilbert invented the first ever electronic cigarette device known as the ‘Smokeless’. The non nicotine device, contained a liquid that was warmed by a battery-powered device, creating a vapor that a person inhaled. Gilbert touted the device’s tremendous potential in preventing disease and death from tobacco use, and even promoted it for weight loss. Dieters, he said, could “smoke their favorite food.” Among the ten vapor flavors he concocted were mint, rum and, his personal favorite, cinnamon.
But Gilbert never found a company willing to mass-produce his invention. We see a classic American tale of an inspired tinkerer way ahead of his time and in 2017, e-cigarettes became a $10 billion USD industry on the global market. Gilbert never made any money on his patent, now long expired. The pressing alarm is that while Gilbert’s invention aimed to be non-nicotine possessed, users today are using all kinds of electronic smoking, and even combining nicotine and THC related properties.
The Study Released By The American Journal of Preventive Medicine
Fast forward to 2019, electronic smoking has been of much concern in the public-health community. Vaping has continued to be questioned whether it is a safer alternative to smoking traditional cigarettes. But the question is, does that potential outweigh their possible risks to human health?
The first study published by the American Journal of Preventive Medicine has found a pressing health issue over users who vape on a daily basis. The study which stated while e-cigarettes are possibly safer than smoking normal cigarettes, users who vaped were about 30% percent more likely to develop chronic lung symptoms such as asthma and emphysema. The study went over the course of three years, 2013 to 2016 with a group of 32,000 adults. The group checked in with no lung related symptoms in 2013. The vaping involved did contain nicotine.
It only took three years for some e-cigarette users to develop chronic lung diseases, according to the first long-term study on the effects of vaping. By 2016, investigators found people who used e-cigarettes were 30 percent more likely to have developed a chronic lung disease, including asthma, bronchitis and emphysema, than nonusers.
The study’s author, Stanton Glantz, of the Center for Tobacco Control Research and Education of the University of California, San Francisco said, “E-cigarette use predicted the development of lung disease over a very short period of time. It only took three years.”
The result of the study made researchers find there was a 1.3-times higher risk of developing respiratory disease than people who did not use any tobacco product. Meanwhile, cigarette smokers had a 2.5-times higher risk, and those who both smoked and vaped had a 3.3-times higher risk.
Was Vaping Ever Considered Safe?
The pressing research continues to fuel the debate within the public-health community whether electronic cigarettes are safer to consume than traditional cigarettes.
Back in 2015, studies conducted by the Public Health of England reported that e-cigarettes are around 95% less harmful than smoking. However, the review raised concerns that increasing numbers of people think e-cigarettes are equally or more harmful than smoking.
“There’s just an incredible disagreement within the public-health community,” – Michael Siegel, a professor at Boston University School of Public Health.
In coming back to the recent study by the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, Dr. Glantz, said, “The great bulk of smokers who use e-cigs are dual users. While it may be true that lung-disease risk might drop, with the caveat that we’re looking at shorter-term effects, that’s not what’s happening.”
What seems large on a wider scale is that there are more pressing variables to take into an account such as a smoker’s past history and whether they are dual users of traditional and electronic smoking.
Ilona Jaspers an inhalation toxicologist from the the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill has studied nearly 20 years in the health effects of many substances that can be inhaled. Seven of those years involved researching e-cigarettes. Jaspers does not believe in the vague idea that vaping is safer than traditional cigarettes because the potential harm seen by vaping is resulting from the chemical compounds contained within the liquid than the nicotine itself. Jaspers asserts,
“When you think about cigarettes, you are looking at the inhalation of a mixture that’s caused by combusting tobacco plants and other chemicals within. Whereas in e-cigarettes, you are aerosolizing a liquid. By definition, that’s a very different exposure. Would you compare cigarettes to smoking crack? No, we don’t. Because we know they’re very different from the get-go.”
E-liquids therefore turn into toxic liquids when heated and vaped. Jaspers explains, “The vast majority of these vaping products contain what we refer to as base compounds. That’s propylene glycol and vegetable glycerin. And when that’s heated to a certain temperature, it actually forms things like acrolein, formaldehyde, acid aldehydes. These are all the chemicals that we know are toxic when inhaled. Just because it’s not there in the base liquid doesn’t mean your lungs will not eventually be exposed to it.”
The Future Of Vaping
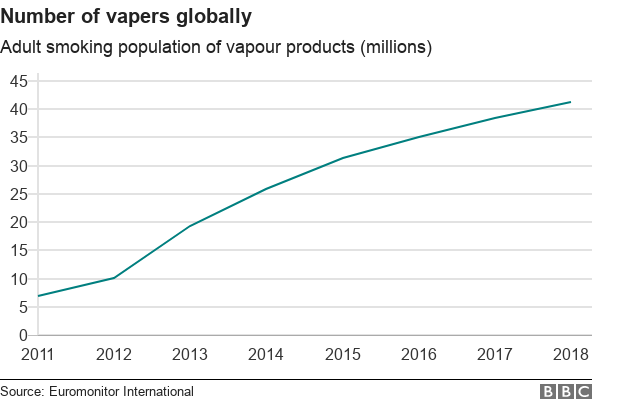
Will this recent study alert the masses of vaping? Maybe, maybe not. The market for e-cigarettes continues to grow exponentially every year, with the BBC reporting users have grown excessively from about seven million in 2011 to 41 million in 2018.
The notion of seeing vaping as safer than traditional smoking was never accepted to be completely health risk free.
A separate study released by the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, on the 16th of December 2019, examined how popular vaping is within the young demographic market. The study that included 14,560 teens found that 75 percent had vaped nicotine, marijuana, or multiple substances. Twelve percent reported vaping within the last 30 days.
These studies by the American Journal of Preventive Medicine should caution audiences and users beyond the public-health community.
Where the US government are having difficulty in addressing the issue of e-cigarette use, because of vaping related to teenage deaths, they have only been trying to ban the vaping device in a number of states. As studies continue, the rising impact of youth culture consuming e-cigarettes remains to be of a crucial importance and one thing remains to be true: electronic smoking isn’t going anywhere.
Subscribe to FIB’s newsletter for your weekly dose of music, fashion and pop culture news!






